Recorded at CDFAM Computational Design Symposium, Berlin, 2024
Presenter: David Heiny
CEO & Co-Founder
Organization: SimScale
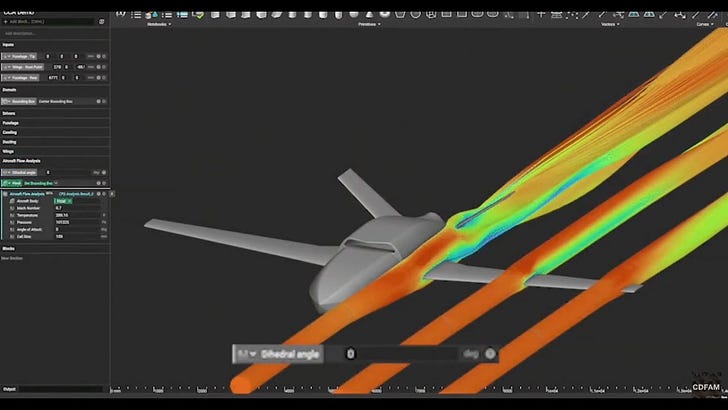
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) in engineering simulation begins a transformative era in product development processes. This presentation outlines the substantial impact of AI adoption in engineering simulation, focusing on how AI models, trained using real and simulated engineering data , can significantly accelerate or even automate future engineering workflows.
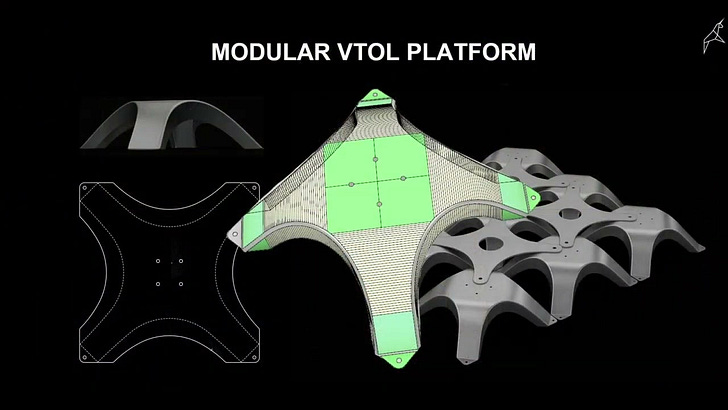
SimScale is developing a pioneering platform in this domain, offering a solution that amalgamates AI with traditional CAE methods. This platform provides accessible tools for both designers and simulation experts, capturing the entire spectrum of AI-enhanced simulation processes and ensures AI future readiness. We present a case study of deploying AI through a cloud-native engineering simulation platform with global engineering teams in the automotive, manufacturing and AEC industries.
The CDFAM Computational Design Symposium Series brings together leading experts from design, engineering, architecture, academia and software development for a series of knowledge sharing and networking events focusing on computational design at all scales.
The events are organized around two foundational frameworks: ‘Scales of Design’ and ‘Dimensions of Execution.’
SCALES OF DESIGN:
Micro: Focus on material-level design considerations
Meso: Exploration of metamaterials and structures
Macro: Discussion on topology optimization, surface and parts
Mega: Exploration of architectural scale system design methodologies
DIMENSIONS OF EXECUTION:
Academic: Cutting-edge research in design science
Algorithm: Software tools and algorithms enabling advanced design
Application: Real-world engineering challenges addressed
Automation: Scaling design to production for volume and mass customization
Through these frameworks, attendees will gain insights into how computational design principles and methodologies traverse across different scales and various execution contexts.